DevOps
PDF-Export-Ansicht unter Google Chrome mit Shortcut 'E' und anschließend Strg+P
DevOps Kultur
Optimizing the human experience
Optimizing the human experience
and performance of operating software...
Optimizing the human experience
and performance of operating software...
with software...
Optimizing the human experience
and performance of operating software...
with software...
and humans.
Optimizing the human experience
and performance of operating software...
with software...
and humans.
Andrew Clay Shafer
Historie
1913
Henry Ford entwickelt "Flow Production"
1930er
Das Toyota Production System wird geboren
1990
"The Machine That Changed the World" von James P. Womack
Historie
2003
Historie
2007
Methode "Agile System Administration"
2008
Andrew Clay Shafer spricht über agile infrastructure
2009
John Allspaw und Paul Hammond"10+ Deploys per Day: Dev and Ops Cooperation at Flickr"
Historie
2009
Patrick Debois und Jean-Paul Sergent organisieren DevOpsDays
Der Rest ist Geschichte.
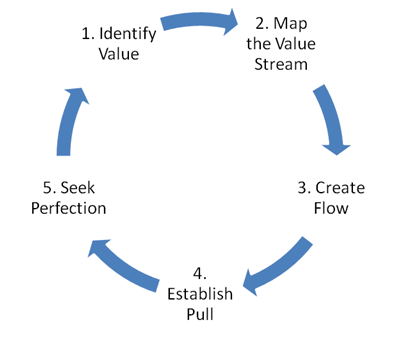
Lean Principles

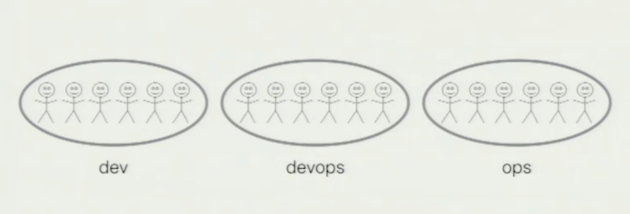
A. Shafer - Wall Of Confusion

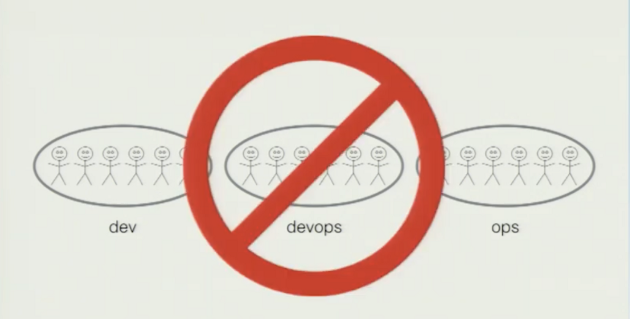
Ein Silo mehr.
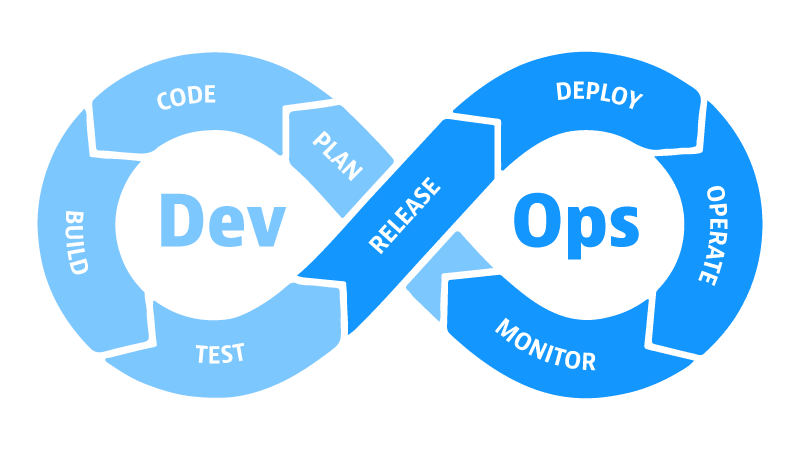
Dev + Ops = DevOps
DevOps Leitsätze
Schaffe eine kollaborative Umgebung.
Automatisiere (fast) alles.
Beobachte kontinuierlich die Ergebnisse.
Fördere ständige Verbesserung.
Habe keine Angst du scheitern. Lerne daraus.
Dein Kunde steht im Mittelpunkt.
Herausforderungen
Dev vs. Ops Mentalität durchbrechen.
Gemeinsames Verständnis schaffen.
Die richtige Automationstrategie finden.
Nicht in Tools verlieren.
Verantwortung an Teams übergeben.
Den Widerstand zur Veränderung überwinden.
Andrew Clay Shafer — What is DevOpsand why should you care?
Methoden
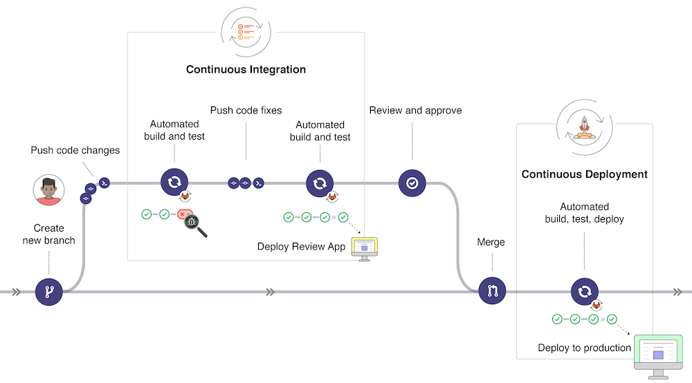
IaC in der Praxis
IaC oder CaC?
Infrastructure as Code
Infrastructure as code (IaC) uses DevOps methodology and versioning with a descriptive model to define and deploy infrastructure, such as networks, virtual machines, load balancers, and connection topologies.
Just as the same source code always generates the same binary, an IaC model generates the same environment every time it deploys.learn.microsoft.com
Configuration as Code
Configuration as code (CAC) is managing configuration resources in your source repository. You treat your application config resources as versioned artifacts.
By managing your application environment in tandem with your application code, you gain the same benefits you get with your code.www.cloudbees.com
Vorteile
Hoher Standardisierungsgrad
Historie über Versionskontrolle
Einfache Rollbacks
Skalierbarkeit
Wiederholbarkeit
Wiederverwendbarkeit
Nachteile
Hoher Initialaufwand
Benötigte Skills
Keine Ad-Hoc Änderungen
Komplexität bei großen Umgebungen
Grundsätze
Versionierungssystem verwenden
Alles in Code umsetzen
Idempotenz
Modulare Codestruktur
Testen, testen, testen

Praxisbeispiel Lab Bonn
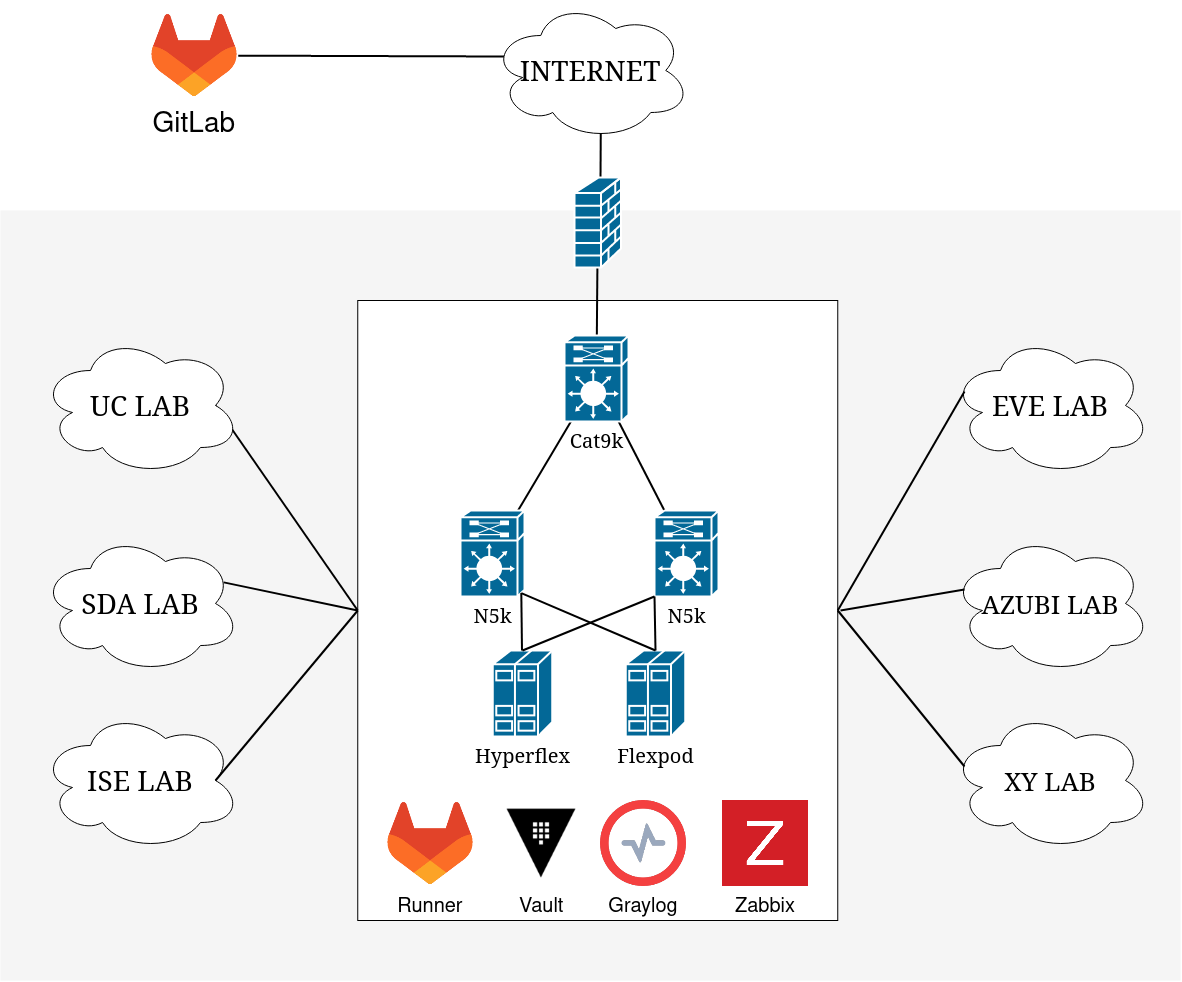
WIP
Kerninfrastruktur
Netzwerk
ASA, Cat9k, Nexus9k
Compute
Hyperflex, Flexpod
Virtual
EVE-NG, ESXi, Docker
Apps
Netbox, Graylog, Zabbix(?), Vault, AD, DNS, DHCP, CA
IaC Komponenten
Source of Truth
Netbox
Versionierung
Gitlab
CI/CD
Gitlab
IaC Komponenten
Secret Management
Hashicorp Vault
Container
Docker, Hashicorp Packer
Configuration
Ansible, Python, Powershell
Python
Powershell
Packer
Gitlab
pyATS
Docker
Vault
VMWare
Zabbix
Plan
Plan
Verwende eine Source of Truth
Dokumentation (in Git)
Abhängigkeiten definießen
Gitlab + Netbox
Code
Code
KISS - Keep it simple stupid
DRY - Don't repeat yourself
Developer+Style Guides
Versionsverwaltung nutzen
IaC Git Workflow
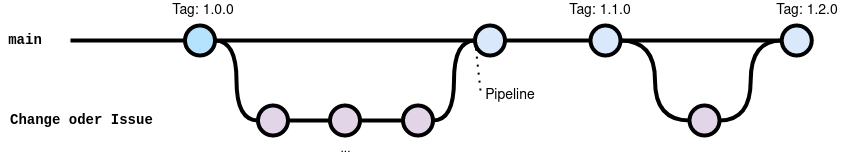
Architekturen
Ansible
- Idempotenz als Leitsatz
- Stärke liegt im Konfigurationsmanagement
- Control Node läuft unter Linux und Mac OS X
- Control Node unter Windows mit WSL
- In Python3 geschrieben
- Master-Less
- Agent-Less
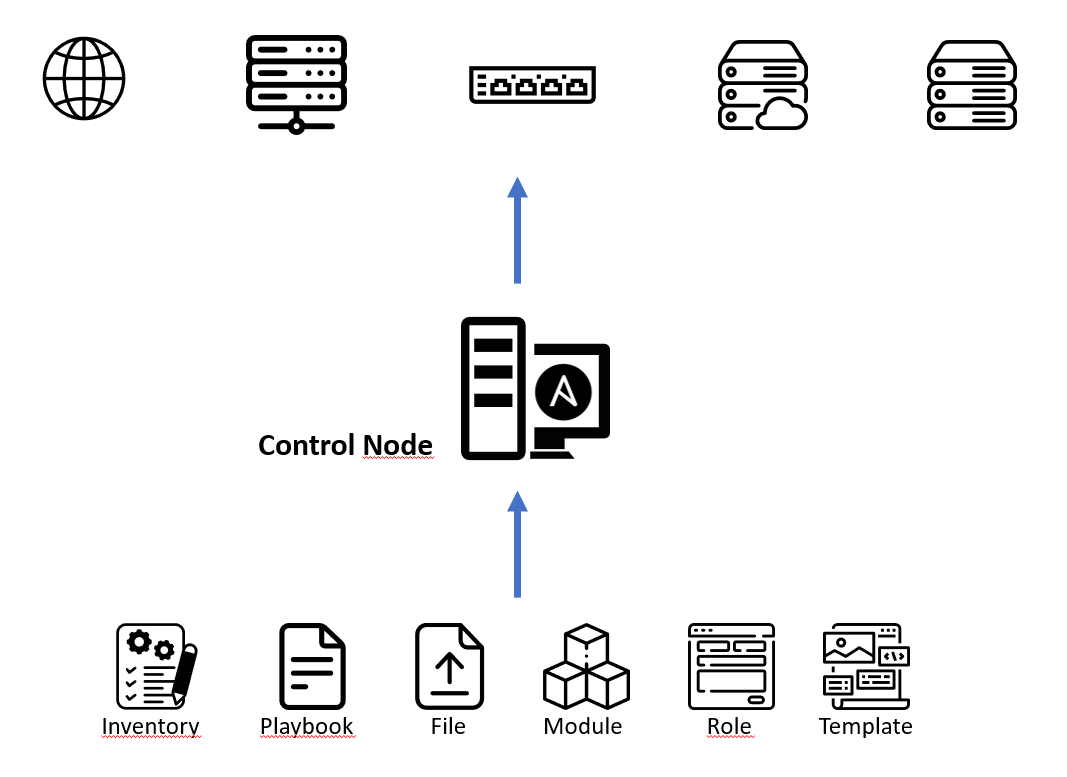
Inventory Dateien
- Zwei Formate: INI und YAML
- Zielsysteme werden üblicherweise gruppiert nach...
- Standort, Funktion, Betriebssystem, usw.
- Mehrere Inventory-Dateien möglich (Dev, Prod, ...)
- Ablage unter ./ oder einem Unterverzeichnis
Prod Inventory
---
all:
children:
lab:
hosts:
shbnlab_core:
dc-n5k-01:
dc-n5k-02:
shbnlab-do01:
docker:
hosts:
shbnlab-do01:
gitlab_runner:
hosts:
shbnlab-do01:
shbnlab-do02:
netbox_docker:
hosts:
shbnlab-do01:
switches:
hosts:
shbnlab_core:
dc-n5k-01:
dc-n5k-02:
Prod Inventory
Übersicht bzw. Gruppe aller Endpunkte.
---
all:
children:
lab:
hosts:
shbnlab_core:
dc-n5k-01:
dc-n5k-02:
shbnlab-do01:
docker:
hosts:
shbnlab-do01:
gitlab_runner:
hosts:
shbnlab-do01:
shbnlab-do02:
netbox_docker:
hosts:
shbnlab-do01:
switches:
hosts:
shbnlab_core:
dc-n5k-01:
dc-n5k-02:
Prod Inventory
Netbox Hosts auf Docker.
---
all:
children:
lab:
hosts:
shbnlab_core:
dc-n5k-01:
dc-n5k-02:
shbnlab-do01:
docker:
hosts:
shbnlab-do01:
gitlab_runner:
hosts:
shbnlab-do01:
shbnlab-do02:
netbox_docker:
hosts:
shbnlab-do01:
switches:
hosts:
shbnlab_core:
dc-n5k-01:
dc-n5k-02:
Prod Inventory
Alle Switches.
---
all:
children:
lab:
hosts:
shbnlab_core:
dc-n5k-01:
dc-n5k-02:
shbnlab-do01:
docker:
hosts:
shbnlab-do01:
gitlab_runner:
hosts:
shbnlab-do01:
shbnlab-do02:
netbox_docker:
hosts:
shbnlab-do01:
switches:
hosts:
shbnlab_core:
dc-n5k-01:
dc-n5k-02:
Build
...
stages:
- build
- test
- staging
- deploy
include:
- template: Security/SAST.gitlab-ci.yml
...
Build
CI Pipeline verwenden
Linting
Containerimages als Artifacts ablegen
Test
...
stages:
- build
- test
- staging
- deploy
include:
- template: Security/SAST.gitlab-ci.yml
...
Test
Testen, testen, testen
EVE-NG als Testplattform für virtualisierte Cisco Komponenten
Testergebnisse speichern
Release+Deploy
...
stages:
- build
- test
- staging
- deploy
include:
- template: Security/SAST.gitlab-ci.yml
...
Release+Deploy
Staging, dann Production
Rollout in Produktion nur von befugten Personen
Nutzung der CD Lösung für Berechtigungskonzept
Operate+Monitor
Operate+Monitor
Alarmierung bei Schwellwertüberschreitungen
Letzte Commits über Alarmmeldungen kommunizieren
Rollbacks über IaC Pipeline durchführen
Demo
Fragen?
Tech Stack
... as Code


Ansible
- Idempotenz als Leitsatz
- Stärke liegt im Konfigurationsmanagement
- Control Node läuft unter Linux und Mac OS X
- Control Node unter Windows mit WSL
- In Python3 geschrieben
- Master-Less
- Agent-Less


Inventory Dateien
- Zwei Formate: INI und YAML
- Zielsysteme werden üblicherweise gruppiert nach...
- Standort, Funktion, Betriebssystem, usw.
- Mehrere Inventory-Dateien möglich (Dev, Prod, ...)
- Ablage unter ./ oder einem Unterverzeichnis
Beispiel Inventory
---
all:
hosts:
dnspublic.domain.com
children:
linux:
hosts:
web1.domain.local:
web2.domain.local:
db1.domain.local:
db2.domain.local:
webservers:
hosts:
web1.domain.local:
web2.domain.local:
databases:
hosts:
db1.domain.local:
db2.domain.local:
dc-emea:
hosts:
web1.domain.local:
db1.domain.local:
dc-asia:
hosts:
web2.domain.local:
db2.domain.local:
Beispiel Inventory
Ein ungruppierter externer DNS-Server.
---
all:
hosts:
dnspublic.domain.com
children:
linux:
hosts:
web1.domain.local:
web2.domain.local:
db1.domain.local:
db2.domain.local:
webservers:
hosts:
web1.domain.local:
web2.domain.local:
databases:
hosts:
db1.domain.local:
db2.domain.local:
dc-emea:
hosts:
web1.domain.local:
db1.domain.local:
dc-asia:
hosts:
web2.domain.local:
db2.domain.local:
Beispiel Inventory
Alle Linux Server in der Umgebung.
---
all:
hosts:
dnspublic.domain.com
children:
linux:
hosts:
web1.domain.local:
web2.domain.local:
db1.domain.local:
db2.domain.local:
webservers:
hosts:
web1.domain.local:
web2.domain.local:
databases:
hosts:
db1.domain.local:
db2.domain.local:
dc-emea:
hosts:
web1.domain.local:
db1.domain.local:
dc-asia:
hosts:
web2.domain.local:
db2.domain.local:
Beispiel Inventory
Nur die Webserver.
---
all:
hosts:
dnspublic.domain.com
children:
linux:
hosts:
web1.domain.local:
web2.domain.local:
db1.domain.local:
db2.domain.local:
webservers:
hosts:
web1.domain.local:
web2.domain.local:
databases:
hosts:
db1.domain.local:
db2.domain.local:
dc-emea:
hosts:
web1.domain.local:
db1.domain.local:
dc-asia:
hosts:
web2.domain.local:
db2.domain.local:
Beispiel Inventory
Nur die Server im EMEA Rechenzentrum.
---
all:
hosts:
dnspublic.domain.com
children:
linux:
hosts:
web1.domain.local:
web2.domain.local:
db1.domain.local:
db2.domain.local:
webservers:
hosts:
web1.domain.local:
web2.domain.local:
databases:
hosts:
db1.domain.local:
db2.domain.local:
dc-emea:
hosts:
web1.domain.local:
db1.domain.local:
dc-asia:
hosts:
web2.domain.local:
db2.domain.local:



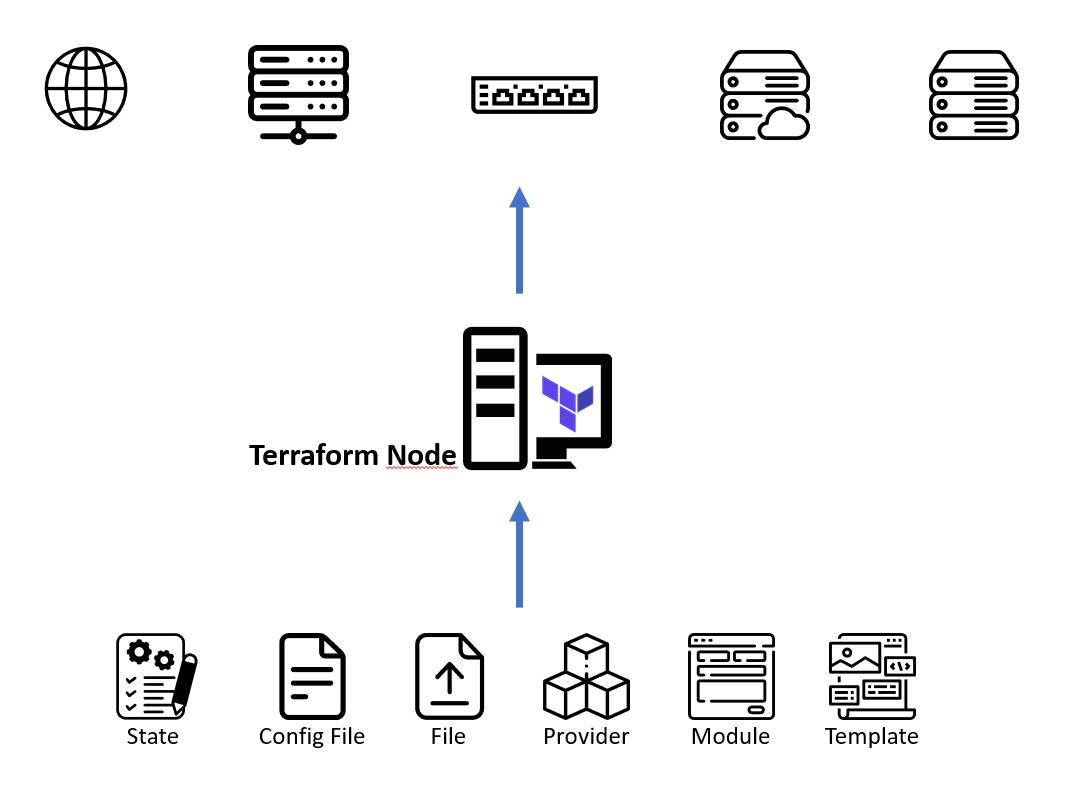
Terraform
- Deklarative Beschreibung des Zielbildes
- Besonders geeignet für Infrastrukturbereitstellung
- Läuft unter macOS, Windows, Linux, BSD, Solaris
- Master-Less
- Agent-Less